The disruption of world economic flows has now reached the phosphate industry. Phosphoric acid is becoming increasingly scarce and increasingly expensive. Considering the enormous economic relevance of phosphoric acid, the current situation is definitely worrying. A short-term easing of the uncertain supply situation is not to be expected due to the escalation of political circumstances.
In this article we look at the current situation regarding the availability of phosphoric acid and where alternative solutions are possible.
Phosphoric acid: A raw material with many applications
The importance of phosphoric acid as one of the most important inorganic chemicals in Europe should not be underestimated. It serves as a feedstock for the production of phosphate-based fertilisers and is used in numerous industrial sectors, including construction, electronics, food and beverages, animal feed, detergents, water treatment, pharmaceuticals and personal care.
A brief overview of the different applications:
- Fertiliser production or use in agriculture.
- Food industry (antioxidant, acidity regulator, flavouring agent), cleaning agent in food technology, tonicity agent in the production of soft drinks and soda drinks, refining of sugars, fats and oils, production of soft drinks and soda drinks
- Nutrient in fermentation
- Wastewater treatment
- Dental treatments (dental cement, etching solutions, tooth whitening, plaque removal)
- Cleaning agents in the construction industry
- Alloy additive for iron and zinc as protection against corrosion
- Rust remover, rust converter
- Wet etchant (semiconductor)
- Flux for soldering
- Etching of silicon nitride (microelectronics)
- Electrolyte in phosphoric acid fuel cells
- Electrolyte in electropolishing copper for deburring
- Production of buffer solutions
- pH-value regulation in hydroponics
- Production of special catalysts, activated carbon, gelatine, hydroxylamine and other pure inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds
Phosphoric acid is used for etching wafers.
Europe is 100 per cent dependent on imports for raw phosphate
Austria, like most countries in the European Union, is almost entirely dependent on imports for phosphate products. Phosphates are mined in Asia, North Africa, North America and the Middle East in ore deposits of varying quality and size.
Around 80 per cent of the raw phosphate mined worldwide is processed directly on site into phosphoric acid or finished fertilisers.
The largest producing countries are China, Morocco and the USA, which together produce two thirds of all phosphates. White phosphorus, which is needed in Europe to produce thermal phosphoric acid, comes from Kazakhstan, Vietnam and China.
Although China has only 5 per cent of the total reserves (3.2 billion tonnes), it is the largest phosphate producer with 90 million tonnes (2020). However, compared to previous years, the country is producing much less (120 million tonnes in 2017) as China's mining and processing industry struggles with environmental fees, higher production costs and shutdowns due to water pollution and other environmental issues.
Most of the world's phosphate reserves are in Morocco, accounting for about 70 per cent of the total (50 billion tonnes). The country is the second largest producer with 37 million tonnes (2020), with most of the production coming from the Bou Craa mine in Western Sahara.
The US is the third largest phosphate producer with 24 million tonnes (2020), although US reserves account for only 2 per cent of global reserves.
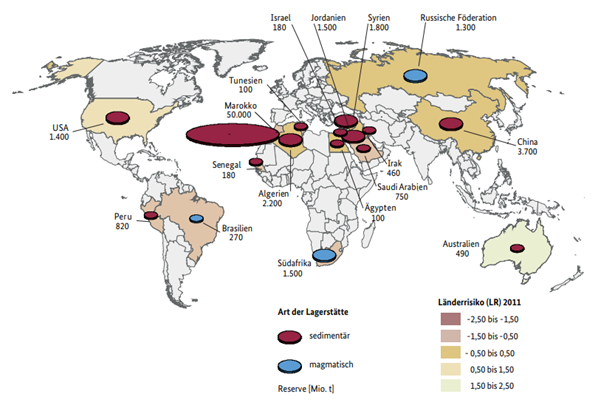
Phosphate reserves worldwide: The world map shows 99 percent of the world's known phosphate deposits with less than 100 million tonnes of phosphate reserves. Source:
BGR
Phosphate rock as the basis of industry
Phosphate rock (rock phosphate) forms the raw material basis for phosphoric acid. The raw phosphate is processed after quarrying and then further processed into phosphoric acid using the wet process or the thermal process.
1. wet process requires sulphuric acid
In the wet process, phosphoric acid is produced by reacting concentrated rock phosphate with sulphuric acid. The wet process produces impure phosphoric acid with a concentration of about 56 per cent, which is used as feedstock for fertilisers, liquid fertilisers and merchant-grade phosphoric acid (MGA). Rock phosphoric acid can also be evaporated to obtain pure phosphoric acid as well as food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade phosphoric acid.
2. thermal process based on white phosphorus
The thermal process of phosphoric acid production involves the combustion of elemental phosphorus to form phosphorus pentoxide and subsequent hydrolysis. Elemental white phosphorus is usually used for the process. Thermal phosphoric acid has a very high purity and is highly relevant for the food and pharmaceutical sectors.

Raw phosphate, mostly apatite, comes largely from deposits outside Europe.
Shortage of raw materials catalyses phosphoric acid prices
The price of phosphoric acid has increased 3 to 4 times since the beginning of 2021 and is currently more than 3,000 euros/tonne. The causes of the shortage or price increase are manifold and, due to their complexity, hardly manageable at present. The statements made here are therefore also subject to certain uncertainties. However, in addition to the availability and price of rock phosphate and white phosphorus, the basic influencing factors are the purchase prices of other key components such as the price of sulphur, energy costs and transport costs.
Supply difficulties with white phosphorus
Several large phosphoric acid producers in Europe are currently experiencing considerable difficulties in procuring white phosphorus from Central Asia. The producers can no longer provide the full quantities. Compensation for the shortfall by other producers does not seem possible at present.
 White phosphorus
White phosphorus,
BXXXD,
CC BY-SA 3.0
High prices for rock phosphate
Prices for rock phosphate have been rising steadily since autumn 2020 and currently stand at 153 euros/tonne (31.1.2022). This corresponds to an increase of 134 percent compared to spring 2020 (65 euros/tonne).
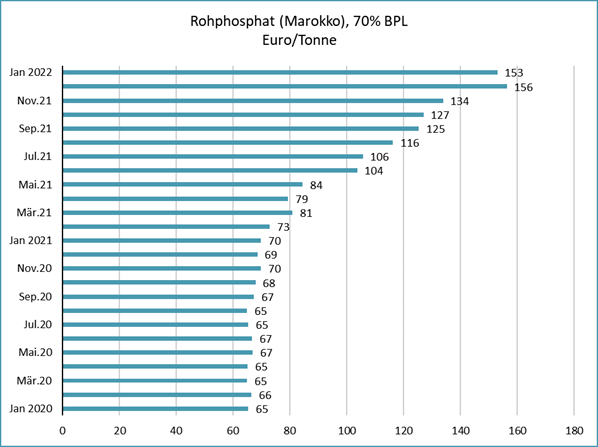
Source:
index mundi
Sulphuric acid available, but expensive
Large quantities of sulphuric acid are needed to produce phosphoric acid by the wet process. With more than 60 per cent of the total world consumption, the production of fertilisers is the most important end-user market for sulphuric acid.
The shortage of sulphuric acid has eased somewhat since last year, but prices are at a high level due to the low production volume of the refineries. Sulphuric acid now has to be converted from elemental sulphur back into liquid sulphur in order to produce sulphuric acid from it.
This drives up sulphuric acid prices and indirectly affects the production costs of phosphoric acid from the wet process.
From Q2 2022 onwards, the situation is expected to worsen as maintenance work is carried out in some refineries. The plants are shut down for three to six weeks, which will again put increasing pressure on the availability of sulphur in Europe.
You can read more about the shortage of sulphuric acid and the associated effects in our blog articles
Sulphuric acid: Why the acid all-rounder is affected by extreme shortages and
Sulphuric acid shortage: Serious impact on industry.
Availability of phosphoric acid remains tight
In our estimation, the glaring undersupply of phosphoric acid in Europe will continue at least until the summer. Even if the supply of raw materials gets back on track in the next few months, the high backlog demand will have a lasting impact on agriculture and various other industries.
Donauchem currently has to quota phosphoric acid, but still has reserves. Due to our good contacts with suppliers and our 2-supplier strategy, we are still able to procure goods for our customers despite the difficult supply situation.
Should the supply situation deteriorate further, we will work out suitable alternatives from our wide range of inorganic acids for individual customers or find an adequate solution. A certain flexibility with regard to possible alternatives is given by Donauchem.
Check alternative acids for your application
A wide range of solutions is available for applications that use phosphoric acid to regulate the pH value (e.g. waste water neutralisation, detergent sector).
One of the possible substitutes is, for example, amidosulfonic acid [S1], which has recently been produced by the Donau Chemie Group in Pischelsdorf. In applications that use phosphoric acid as a nutrient, substitution with another acid is not possible. However, a reduction of the quantity consumption can be aimed at, for example in agriculture.
Conclusion: Regional alternatives for phosphoric acid
From today's perspective, an easing of the raw material situation is not to be expected in the near future. In view of the unstable situation on the global raw material markets, it is worth considering regional phosphoric acid alternatives. In many areas of application, it is possible to replace phosphoric acid with other inorganic acids. Feel free to contact us to explore the options for your application and work out a suitable solution.
Due to the current political situation, an easing of the current phosphoric acid situation is not in sight!
 www.donauchem.at
www.donauchem.at