Behind the scenes at Donauchem: How quality and safety go hand in hand in distribution and contract manufacturing
The chemical industry is subject to numerous legal regulations and industry-specific standards. Effective quality control and quality assurance ensures compliance with these requirements and is crucial to ensuring high product quality and customer satisfaction. Oliver Groß, Head of Quality Assurance at Donauchem, provides you with insights into the central tasks and processes of quality control and quality assurance at Donauchem.
Quality management, quality control, quality assurance - what is the difference?
An apt comparison to delineate these terms is the components of a bicycle:
While quality management represents the handlebars and sets the strategic direction, product-related quality control and process-oriented quality assurance are the two wheels that keep the system moving:
- Quality control specifically refers to checking product quality by taking samples and subjecting them to various tests.
A detailed sample plan exists that sets specific analysis parameters and prescribes predefined equipment on which the tests are carried out. The steps of this process are precisely structured and defined to ensure that all aspects of quality testing are carried out efficiently and accurately.
- Quality assurance, on the other hand, defines the processes, procedures and methods needed to ensure quality along the entire value chain of Donauchem.
- In addition, Quality Management monitors and reviews all areas that have a direct or indirect impact on customer satisfaction, implements risk mitigation procedures, oversees employee training and conducts internal audits to ensure compliance with quality standards.
A clear separation of these tasks is not always possible at Donauchem, as the transitions are fluid and quality control also takes over aspects of quality assurance from quality management. All three areas work closely together to ensure consistently high product quality. The focus of the following explanations is primarily on quality control.
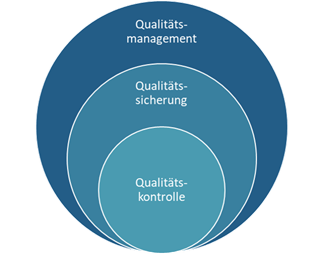
Figure 1: QM, QA and QC work in synergy to ensure quality in Donauchem's chemical distribution and contract manufacturing.
Legal regulations and standards: Foundation of quality control
The tasks of quality control are extremely diverse and demanding. A central component consists of carefully checking product quality against the specific requirements laid down not only in the applicable laws and standards, but also in the individual agreements with our customers.
1. Legal requirements
In certain product areas, such as food and food additives, there are EU regulations that set specific parameters and requirements that must be met as minimum quality standards.
The situation is similar for medicinal products and their precursors, which are listed in the European Pharmacopoeia. In Austria, in addition to the Austrian Pharmacopoeia (ÖAB), the EU Pharmacopoeia (Ph.Eur.) is used as a recognised reference for the quality and standards of medicinal products.
For technical chemicals, on the other hand, the legislator leaves the scope for defining quality standards relatively wide open. Specifications can be set according to need and application.
This means that the quality of products from pharmaceutical quality to technical quality is subject to a wide range and is individually agreed with our customers.
2. Relevant standards
To ensure that high quality standards are maintained, Donauchem implemented a comprehensive quality management system as early as 1995. This system covers all company sites and is certified according to the current version of ISO 9001. In addition to this certification, we have acquired further certifications in various areas:
- ISO 22000: This standard deals specifically with food safety and ensures that the appropriate requirements and control mechanisms are implemented to guarantee the safety of the food produced.
- Responsible Care®: Donauchem participates in the Responsible Care initiative, a global initiative of the chemical industry that focuses on environmental protection, health and safety.
- RSPO: Donauchem sources palm oil products from sustainably managed palm plantations that are certified according to the standards of the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO).
Location
|
Certified according
to EN ISO 9001
|
Certified according
to ISO 22000 (Food) |
Certified according to
Responsible Care
|
Certified according to
RSPO criteria
|
| Donauchem |
since 1995 |
|
|
|
Brückl site
(established 2022) |
since 2022
|
since 01/2023
|
in planning
|
|
Pischelsdorf site
(established 2008) |
since 2008
|
since 2019
(before that HACCP) |
since 2015
|
since 2019
|
Figure 2: A total of 15 internal auditors with different specialisations in the areas of quality assurance, environment, hygiene and safety ensure that the standards are met internally.
3. Individual quality agreements
Quality control not only monitors compliance with legal regulations and standards, but also individual quality agreements with customers. These agreements may contain specific requirements that go beyond mere specifications.
An example of this is the labelling of products. For example, if the customer wants a delivery with a red marking, it is the responsibility of quality control to ensure that this marking is done correctly.
In addition, customers may have special delivery requirements, such as the provision of an external certificate. In such cases, quality control staff draw a sample that is sent to an external body and analysed to provide the necessary documents for delivery.
Quality control thus plays a crucial role in meeting individual customer requirements and ensures that all aspects of quality are met according to the agreements made.
The three phases of quality control
The quality control process is divided into three independent processes: Quality control at goods receipt, during production and at goods issue. Every single product goes through a meticulous analysis process, during which we ensure that it meets the specified quality guidelines and agreed quality requirements.
1. Incoming goods inspection
During the incoming goods inspection, the goods are thoroughly inspected upon arrival and the associated certificates are checked. The focus is on a quick assessment or, if necessary, sampling and analysis of basic parameters to verify the identity and quality of the delivered goods. In the case of tank wagons, samples are given priority so that the tank can be unloaded as quickly as possible.
In the course of quality control, we check each chamber of the tank truck and look at representative physical parameters such as content, density, refractive index or, for example, the water content in the case of solvents.
Based on these parameters, we can quickly determine whether the goods meet our specifications and can be released for processing, storage or further transport.
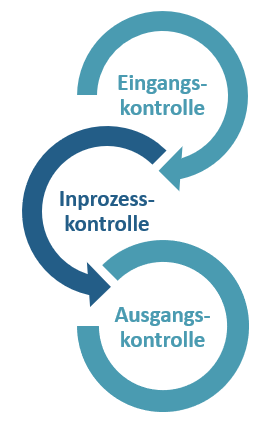
2. In-process control
In-process controls are an essential part of the production process and are used to ensure that the product being manufactured meets the established specifications.
Sampling is carried out during ongoing production and is particularly relevant for complex blends where certain parameters need to be adjusted.
# Checking and adjusting parameters
An important output of in-process control is to identify and correct deviations from limits in the specified parameters.In such cases, it is critical to determine the causes and investigate whether there may be incorrect specification values.
Take, for example, a mixture where a certain pH value is to be achieved. If this pH value is reached in only five out of ten cases, regardless of whether it is acidic or alkaline, it can be checked whether the amount of acid or alkali needs to be adjusted to specifically reach the desired range. This would be a classic process optimisation based on the determined data from the quality control.
The use of data from quality control thus enables targeted control of processes in order to achieve the desired output.By regularly checking and adjusting the relevant parameters, it is ensured that the end product meets the desired quality standards and satisfies the customer's requirements.
# Cleaning of mixing vessels
Another application of in-process control is in the area of cleaning.
Not only for products from the food or pharmaceutical sector, the mixing containers must be thoroughly cleaned in advance and the cleaning documented. A sample is taken and checked in the laboratory for certain parameters.Only after a successful inspection is the mixing container released for production.
In addition, the quality assurance department checks and archives the cleaning checklists that are filled out by the employees in the course of cleaning the respective area.
3. Outgoing goods inspection
The outgoing goods inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring that the goods meet the required quality standards before they are shipped. In addition to the visual inspection of the goods and ensuring batch tracing, this area of responsibility also includes the preparation of analysis certificates, shipping documentation and, in an extended sense, the outgoing goods check for hazardous goods transports:
# Batch tracing
In our mixing area, we subject every ready-mixed product to comprehensive sampling and analysis on a batch basis before it is filled.A sample of each blended batch is taken and thoroughly examined.
After inspection, the mix is filled into containers, creating multiple batches. Each of these batches is given a unique batch number, which is also mapped in the ERP system and refers to the original mixture.
Retention samples serve as comparison material for later productions and can be used for investigation in case of customer complaints or other quality problems.
# Certificates of analysis 
In the course of the outgoing inspection, the quality control department issues certificates of analysis for our customers, which provide information on the analysed parameters of the product.
The certificates are issued in paper form and attached to the deliveries together with the delivery note, which is also the dangerous goods transport document. Often, the certificate is also automatically sent to the customer by e-mail via our laboratory database.
These customers thus receive the certificate of analysis before the goods arrive.
# Photo documentation
As part of the outgoing inspection, photos are taken of each container, pallet or IBC to document the condition of the goods. These photos serve as visual evidence of the quality of the products before delivery.
# Outgoing check for dangerous goods transports
In addition to the aforementioned quality control tasks, Quality Assurance ensures that the outgoing checks for dangerous goods transports are carried out and that the trucks are inspected:
- Checking the packaging and dangerous goods labelling (labels, safety instructions).
- Documentation and checking of transport documents (dangerous goods transport document, analysis certificates).
- Inspection of transport vehicles and equipment (inspection of vehicles for their safety equipment and emergency equipment specific to dangerous goods).
About 95 percent of our trucks transport dangerous goods. Every employee in QC and QA therefore undergoes a one-week external training course to become a dangerous goods officer, which is refreshed every 5 years.
Sample production in quality control
In the laboratory, in addition to our regular tasks, we also carry out the production of customer samples. This means that we either sample individual raw materials, where an employee from the department takes a sample from a stored container, or we also produce mixtures for customers in the quality control laboratory.
For more complex blends, the involvement of the R&D department is necessary as special requirements and specifications have to be taken into account. For simpler mixtures or dilutions, the samples can be made directly in the control laboratory.
In some cases, sample production is only focused on determining certain parameters for specifications or safety data sheets.An example of this is checking the pH of a mixture to determine whether it is alkaline, neutral or acidic. These analyses provide us with important information about the properties of the mixture and can ensure that it meets the required standards.
The determination of such parameters is important both for quality assurance and for meeting legal requirements, especially with regard to safety aspects.
Seamless traceability: the role of QA and QC
Another essential task of QA and QC is the seamless tracking and documentation of all relevant data and information along the entire production and delivery process. The tasks between QC and QA are divided as follows:
- Quality control tasks: ensuring traceability of samples, tests and results by keeping records of sampling, analytical methods, equipment used, tests performed and other relevant details.
Quality assurance tasks: identifying and labelling products (batch/serial number), documenting relevant data and information (raw materials, processed products, procedures, production process, customer deliveries), and establishing records and traceability chains.
Traceability is highly relevant for the fulfilment of legal requirements and standards, especially with regard to product liability. It makes it possible to react quickly and take appropriate measures in the event of complaints.
Efficient complaints management at Donauchem
Complaint management at Donauchem is an integral part of the quality management system (QMS) and is handled by QA and QC. It covers various aspects such as raw materials, customer complaints and internal complaints:
1. Customer complaints
1. customer complaints
Customer complaints sometimes concern transport damage, such as leaking canisters that were damaged during the handling and transport process. When analysing the cause, we check whether the damage was caused by improper handling, defective pallets or impacts during transport. By comparing the photos from the outgoing inspection with the customer's pictures, we can quickly identify the cause of the damage and take appropriate action.
In addition, deviations from the desired quality standard can occur on the chemical side, such as impurities. In such cases, quality control plays a decisive role by determining whether the product actually deviates from the expected quality by resorting to laboratory values or comparing the product complained about with the return sample.
Complaints are also frequently made on the basis of specific characteristics of the product which, however, sometimes do not represent a clear defect at all. A good example of this is discolouration: For example, the product data sheet describes the product as a "water-clear to yellowish solution". If the customer now receives a product that appears water-clear several times, but a yellowish solution once, this could lead to a complaint, even though the product is within the defined specifications.
At Donauchem, we have designated responsibilities for each type of customer complaint so that a statement to the customer concerned is recorded within a set time frame. This includes the course of the problem and the measures taken for improvement. Through this approach, we continuously optimise our processes and meet the requirements of ISO 9001.
|
Product data sheet
|
Safety data sheet
|
The primary purpose of the product data sheet (PDB) is to provide the customer with information about the product and its properties.
The PDB contains technical data such as physical and chemical properties, application instructions, storage recommendations and handling information.
|
The safety data sheet (SDS) focuses on the safety and handling of the product. It serves as a rough guide and is usually limited to information on the raw materials used.
The SDS provides detailed information on the potential hazards that may arise from a substance or mixture, measures to avoid risks and first aid in case of emergency. |
Figure 5: The difference between product and safety data sheet.
2. Internal complaints
Internal complaints are also considered within the framework of complaints management. If deviations occur within the company that affect the proper functioning of processes, workflows or results, these are treated as internal complaints.
3. Raw material complaints
With regard to raw materials, complaints can arise when delivered goods do not meet the required specifications or show transport damage. As already described, the raw materials are checked by the QC in the course of the incoming inspection.
When dealing with raw material complaints, the further procedure must be agreed upon with the purchasing department, the transporter and the supplier.
Conclusion: Quality along the value chain
Quality control and quality assurance are of central importance for chemical distribution and contract manufacturing and are inseparably linked. Our quality control monitors and tests product quality, while quality assurance defines the necessary processes and procedures to ensure this quality along the entire value chain. As essential elements of our quality management system, they play a key role in ensuring that we can offer and deliver products of high quality and safety to our customers.
We look forward to supporting you with our products in the future. If you have any enquiries, we are always there for you -
contact us today.
 www.donauchem.at
www.donauchem.at